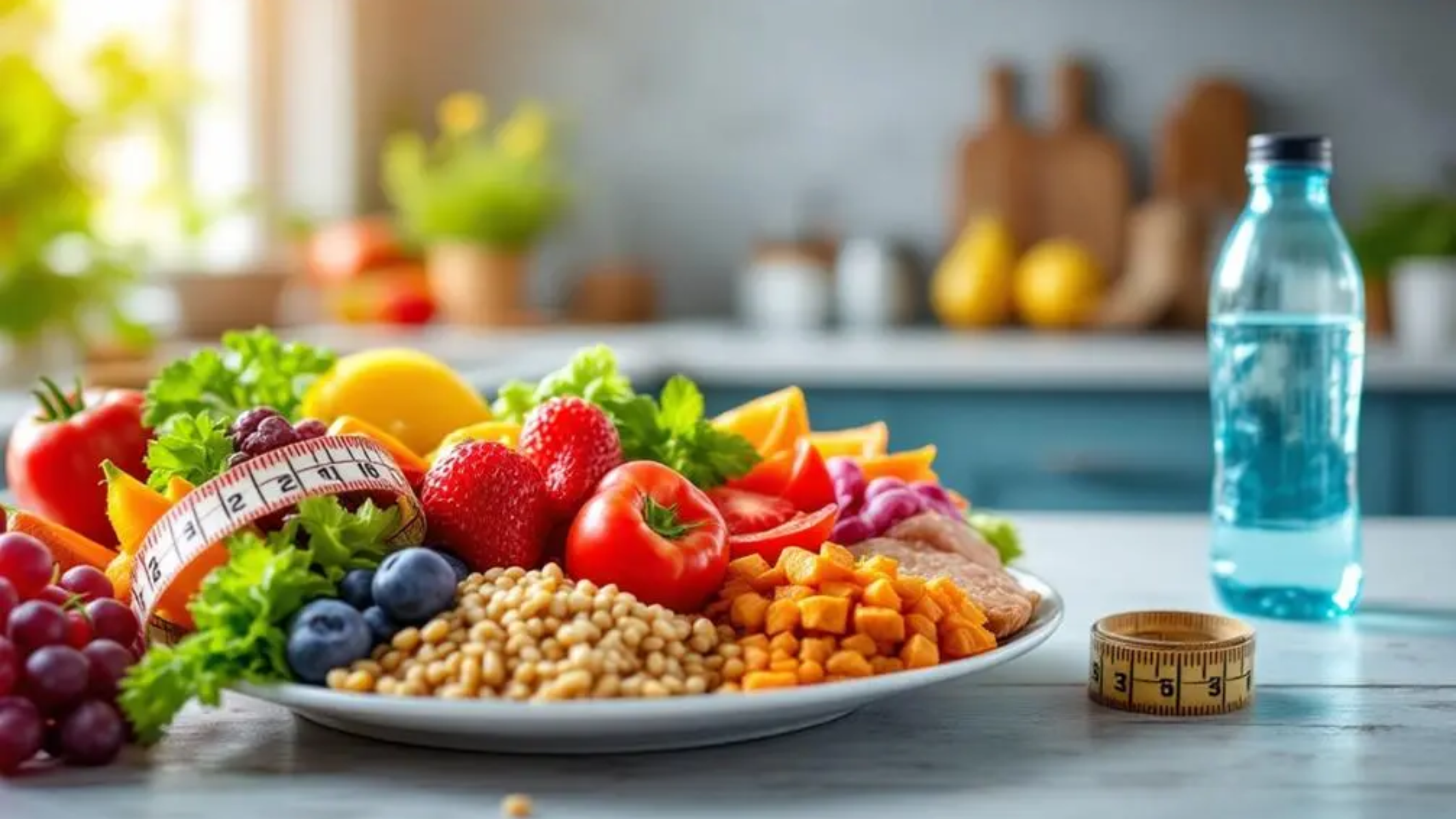
When we think about nutrition for weight loss and digestive health, protein, and healthy fats often steal the spotlight. But a quiet powerhouse in your diet deserves recognition: fiber. This unsung hero offers a trifecta of benefits—promoting digestive health, relieving bloating, and aiding in weight loss.
What is Fiber?

Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body can’t digest. Found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, fiber comes in two forms:
- Soluble Fiber: Dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that slows digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insoluble Fiber: Adds bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
1. Digestive Health: Keeping Things Moving
Fiber plays a critical role in maintaining a healthy digestive system:
- Prevents Constipation: Insoluble fiber ensures that food moves smoothly through your digestive tract.
- Nourished Gut Bacteria: Soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in your gut. A balanced microbiome supports better digestion and overall health.
- Reduces Risk of Digestive Disorders: A high-fiber diet has been linked to a lower risk of conditions like diverticulitis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
2. Bloating Relief: Say Goodbye to Discomfort
Bloating can be caused by irregular digestion or gas buildup in the gut. Fiber helps by:
- Promoting Regularity: Regular bowel movements prevent gas and bloating caused by food lingering too long in your system.
- Improving Gut Health: A healthy gut microbiome reduces gas production, easing bloating.
- Balancing Water Retention: Soluble fiber can help regulate water absorption, reducing feelings of bloating.
3. Weight Loss: Fiber as Your Secret Weapon
Fiber can be a game-changer in your weight loss journey. Here’s why:
- Increases Satiety: High-fiber foods take longer to chew and digest, making you feel fuller for longer and reducing the urge to snack.
- Regulates Blood Sugar: Fiber slows the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes and crashes that trigger cravings.
- Lower Calorie Density: Fiber-rich foods are typically lower in calories but high in volume, helping you eat less without feeling deprived.
How to Add More Fiber to Your Diet
- Start Small: Gradually increase fiber intake to avoid discomfort.
- Diversify Sources: Include a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Fiber works best when paired with adequate water intake.
Daily Fiber Recommendations
- Women: At least 25 grams per day.
- Men: At least 38 grams per day.
Despite its importance, most people consume only half of the recommended amount.
Final Thoughts
Fiber is the unsung hero your body needs for optimal health, from aiding digestion and relieving bloating to supporting weight loss. Making fiber-rich foods a staple in your diet will make you feel better and set the stage for long-term wellness.